【Spring Boot】整合 AOP
1 认识 Spring AOP
1.1 什么是 AOP
AOP (Aspect Oiented Programn, 面向切面编程)把业务功能分为核心、非核心两部分。
- 核心业务功能: 用户登录、增加数据、删除数据。
- 非核心业务功能: 性能统计、日志、事务管理。
在 Spring 的面向切面编程 (AOP) 思想里,非核心业务功能被定义为切面。核心业务功能和切面功能先被分别进行独立开发,然后把切面功能和核心业务功能“编织”在一起,这就是
AOP。
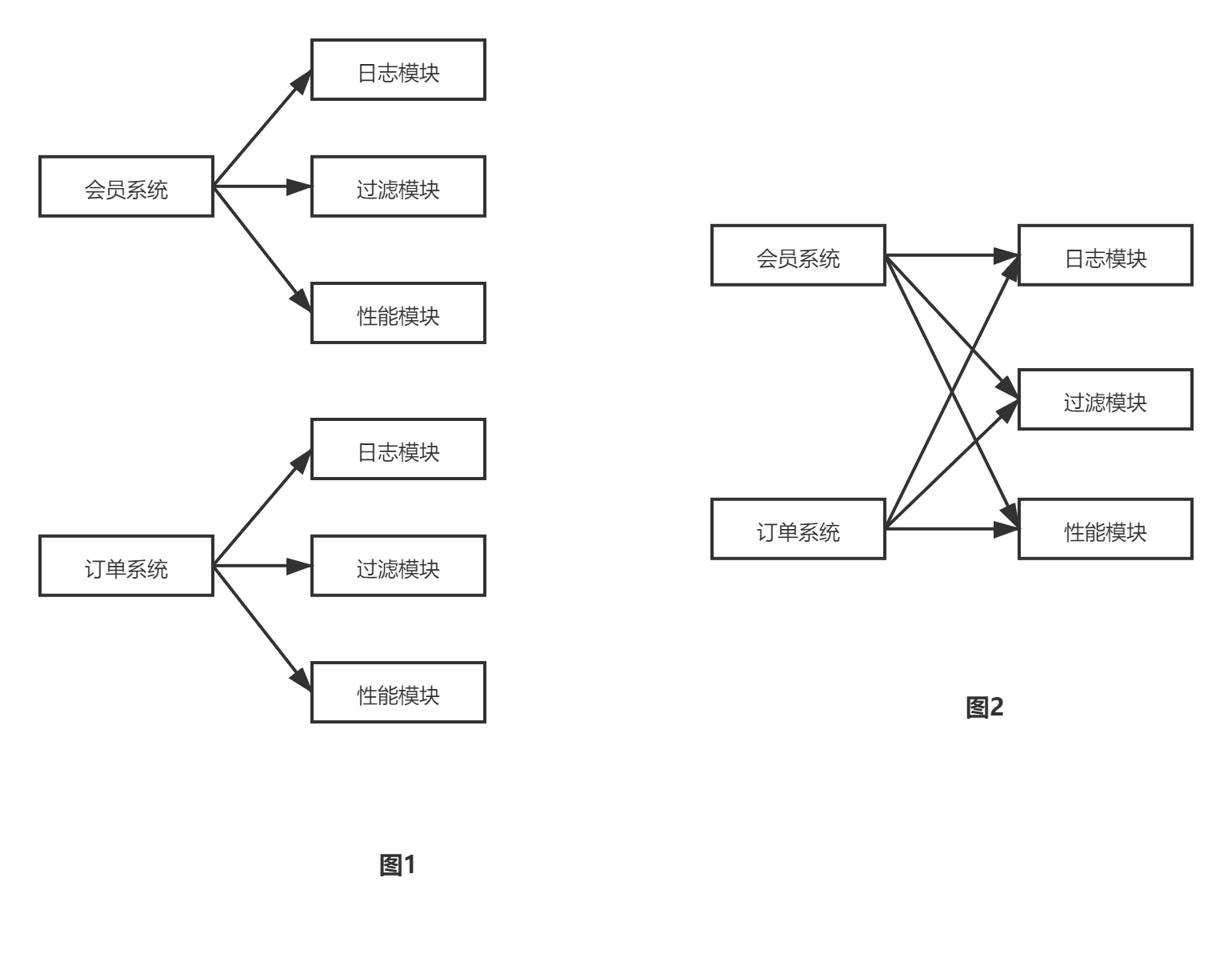
未使用 AOP 的程序如 图 1 所示,使用 AOP 的程序如 图 2
所示。由此可见,AOP 将那些与业务无关,却为业务模块所共同调用的逻辑封装起来,以便减少系统的重复代码,降低模块间的耦合度,利于未来的拓展和维护。这正是
AOP 的目的,它是 Spring 最为重要的功能之一,被广
泛使用。
1.2 AOP 中的概念
切入点(pointcut):在哪些类、哪些方法上切入。
通知(advice):在方法前、方法后、方法前后做什么。
切面 = 切入点 + 通知。即在什么时机、什么地方、做什么。
织入(weaving):把切面加入对象,并创建出代理对象的过程
环绕通知(around):AOP 中最强大、灵活的通知,它集成了前置和后置通知,保留了连接点原有的方法。
AOP 的体系可以梳理为下图: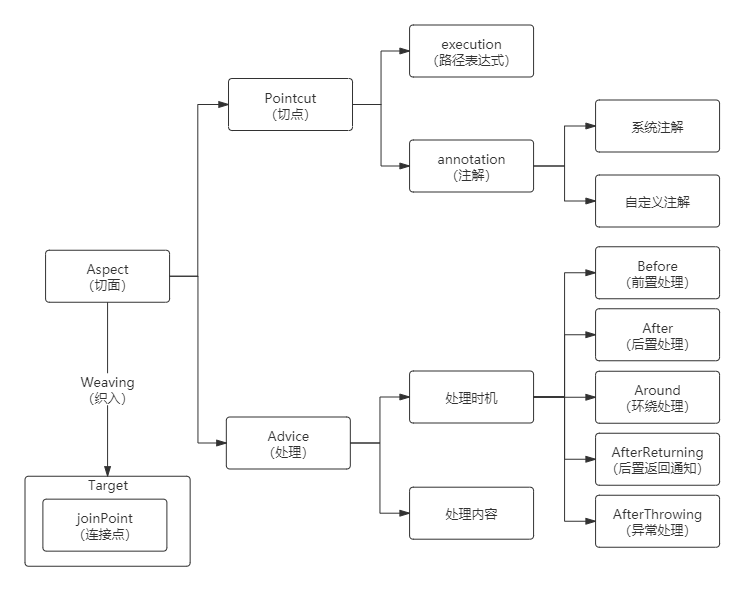
2 AOP 代码示例
首先导入 AOP 的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>2.1 使用 execution(路径表达式)
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogAspect {
ThreadLocal<Long> startTime = new ThreadLocal<>();
/**
* execution 函数用于匹配方法执行的连接点,语法为:
* execution(方法修饰符(可选) 返回类型 方法名 参数 异常模式(可选))
* 参数部分允许使用通配符:
* * 匹配任意字符,但只能匹配一个元素
* .. 匹配任意字符,可以匹配任意多个元素,表示类时,必须和 * 联合使用
* + 必须跟在类名后面,如 Horseman+,表示类本身和继承或扩展指定类的所有类
*/
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.example.aop_demo.controller.*.*(..))")
private void webLog() {
}
/**
* 前置通知:在目标方法被调用之前调用通知功能
*/
@Before("webLog()")
public void doBefore(JoinPoint jp) {
System.out.println("=====================doBefore======================");
// 接收到请求
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
// 记录请求内容
log.info("URL : {}", request.getRequestURL());
log.info("HTTP 方法 : {}", request.getMethod());
log.info("IP 地址 : {}", request.getRemoteAddr());
log.info("类的方法 : {}.{}", jp.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName(), jp.getSignature().getName());
log.info("方法参数 : {}", Arrays.toString(jp.getArgs()));
System.out.println("=====================doBefore======================");
}
/**
* 返回通知:在目标方法成功执行之后调用通知
*/
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "webLog()", returning = "result")
public void doAfterReturning(Object result) {
System.out.println("=====================doAfterReturning======================");
// 处理完请求,返回内容
System.out.println("方法的返回值 :" + result);
System.out.println("=====================doAfterReturning======================");
}
/**
* 最终通知:在目标方法完成之后调用通知,不管是抛出异常或者正常退出都会执行
*/
@After("webLog()")
public void doAfter(JoinPoint jp) {
System.out.println("=====================doAfter======================");
System.out.println("方法最后执行.....");
System.out.println("=====================doAfter======================");
}
/**
* 环绕通知:通知包裹了被通知的方法,在被通知的方法调用之前和调用之后执行,相当于 MethodInterceptor
*/
@Around("webLog()")
public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) {
System.out.println("=====================doAround======================");
System.out.println("方法环绕 start.....");
startTime.set(System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Object o = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("方法环绕 proceed,结果是 :" + o);
System.out.println("方法执行耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime.get()) + "ms");
System.out.println("=====================doAround======================");
return o;
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* 异常通知:在目标方法抛出异常后调用通知
*/
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "webLog()", throwing = "ex")
public void doThrows(JoinPoint jp, Exception ex) {
System.out.println("=====================doThrows======================");
System.out.println("方法异常时执行 \n 发生的异常:" + ex.getClass().getName() + "\n 异常信息:" + ex.getMessage());
System.out.println("=====================doThrows======================");
}
}controller 代码如下,返回当前日期时间
@RestController
public class BaseController {
@GetMapping("/api1")
public Map<String, Object> api1() {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(16);
map.put("nowTime", LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")));
return map;
}
}调用接口,控制台输出结果如下:
===================== doAround ======================
方法环绕 start.....
===================== doBefore ======================
2021-05-09 23:20:58.013 INFO 14772 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] com.example.aop_demo.aop.LogAspect: URL: http://192.168.85.1:8080/api1
2021-05-09 23:20:58.014 INFO 14772 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] com.example.aop_demo.aop.LogAspect: HTTP 方法: GET
2021-05-09 23:20:58.014 INFO 14772 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] com.example.aop_demo.aop.LogAspect: IP 地址: 192.168.85.1
2021-05-09 23:20:58.015 INFO 14772 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] com.example.aop_demo.aop.LogAspect: 类的方法: com.example.aop_demo.controller.BaseController.api1
2021-05-09 23:20:58.016 INFO 14772 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] com.example.aop_demo.aop.LogAspect: 方法参数: []
===================== doBefore ======================
===================== doAfterReturning ======================
方法的返回值 : {nowTime=2021-05-09 23:20:58}
===================== doAfterReturning ======================
===================== doAfter ======================
方法最后执行.....
===================== doAfter ======================
方法环绕 proceed,结果是 : {nowTime=2021-05-09 23:20:58}
方法执行耗时:18ms
===================== doAround ======================代码解释如下:
@Aspect:标记为切面类
@Component:把切面类加入 IoC 容器中,让 Spring 进行管理
@Before:再切入点开始处切入内容。
@After:在切入点结尾处切入内容
@AfterReturning:在切入点返回内容之后切入内容,可以用来对处理返回值做一些加工处理。
@Around:在切入点前后切入内容,并控制何时执行切入点自身的内容。
@AfterThrowing:用来处理当切入内容部分抛出异常之后的处理逻辑。
注: - 被 @Around 标注的方法,必须要有一个 ProceedingJoinPoint 类型的参数,其他的可以不加参数 - @Order 用于指定 Spring
IOC 容器中 Bean 的执行顺序的优先级(不是定义 Bean 的加载顺序),值越小拥有越高的优先级,可为负数。
源码如下: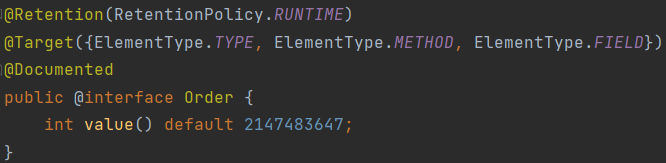
2.1 使用 annotation(注解)
首先定义一个注解(不想自定义注解使用系统注解也可以,比如 @GetMapping)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String value() default "";
}定义切面
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class AnnotationAspect {
ThreadLocal<Long> startTime = new ThreadLocal<>();
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.example.aop_demo.annotation.MyAnnotation))")
private void myAnnotationCheck() {
}
@Before("myAnnotationCheck()")
public void doBefore(JoinPoint jp) {
System.out.println("=====================doBefore======================");
startTime.set(System.currentTimeMillis());
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
log.info("URL: {}", request.getRequestURL());
log.info("HTTP 方法: {}", request.getMethod());
log.info("IP 地址: {}", request.getRemoteAddr());
log.info("类的方法: {}.{}", jp.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName(), jp.getSignature().getName());
log.info("方法参数: {}", Arrays.toString(jp.getArgs()));
System.out.println("=====================doBefore======================");
}
/**
* 后置增强
*/
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "myAnnotationCheck()", returning = "result")
public void doAfterReturning(Object result) {
System.out.println("=====================doAfterReturning======================");
log.info("方法的返回值 : {}", result);
log.info("耗时 : {} ms", (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime.get()));
System.out.println("=====================doAfterReturning======================");
}
}controller 代码如下,先阻塞两秒,观察耗时
@RestController
public class BaseController {
@MyAnnotation
@GetMapping("/api2")
public String api2() throws InterruptedException {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
return "api2 调用成功";
}
}执行结果如下:
=====================doBefore======================
2021-05-09 23:43:47.144INFO 14772---[nio-8080-exec-3]com.example.aop_demo.aop.AnnotationAspect: URL :http://192.168.85.1:8080/api2
2021-05-09 23:43:47.144INFO 14772---[nio-8080-exec-3]com.example.aop_demo.aop.AnnotationAspect: HTTP 方法 :GET
2021-05-09 23:43:47.144INFO 14772---[nio-8080-exec-3]com.example.aop_demo.aop.AnnotationAspect: IP 地址: 192.168.85.1
2021-05-09 23:43:47.145INFO 14772---[nio-8080-exec-3]com.example.aop_demo.aop.AnnotationAspect: 类的方法: com.example.aop_demo.controller.BaseController.api2
2021-05-09 23:43:47.145INFO 14772---[nio-8080-exec-3]com.example.aop_demo.aop.AnnotationAspect: 方法参数: []
=====================doBefore======================
=====================doAfterReturning======================
2021-05-09 23:43:49.152INFO 14772---[nio-8080-exec-3]com.example.aop_demo.aop.AnnotationAspect: 方法的返回值: api2 调用成功
2021-05-09 23:43:49.152INFO 14772---[nio-8080-exec-3]com.example.aop_demo.aop.AnnotationAspect: 耗时: 2008 ms
=====================doAfterReturning======================获取注解属性的方法:
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
myAnnotationCheck annotation = signature.getMethod().getDeclaredAnnotation(myAnnotationCheck.class);
// 获取 value 属性
String value = annotation.value();3 JoinPoint 对象
JoinPoint 对象封装了 SpringAop
中切面方法的信息 , 在切面方法中添加 JoinPoint 参数, 就可以获取到封装了该方法信息的 JoinPoint 对象.。
方法名功能 Signature getSignature() 获取封装了署名信息的对象, 在该对象中可以获取到目标方法名, 所属类的 Class 等信息 **
Object[] getArgs() 获取传入目标方法的参数对象 Object getTarget() 获取被代理的对象 Object getThis()
获取代理对象 **
4 ProceedingJoinPoint 对象
ProceedingJoinPoint 对象是 JoinPoint 的子接口,** 该对象只用在 @Around 的切面方法中 **
方法名功能 Object proceed()throws Throwable** 执行目标方法 **Object proceed(Object[] var1) throws Throwable
传入的新的参数去执行目标方法
5 使用了环绕通知后,全局异常捕获失效的解决办法
观察环绕通知代码,发现异常被环绕通知给捕获了
@Around("apiLog()")
public void logAround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) {
System.out.println("=====================doAround======================");
try {
// 将控制权交给被通知的方法
pjp.proceed();
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("=====================doAround======================");
}解决方法就是抛出这个异常,具体操作就是给方法加上 throws Throwable
@Around("apiLog()")
public void logAround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("=====================doAround======================");
// 将控制权交给被通知的方法
pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("=====================doAround======================");
}部分参考
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_15037231/article/details/80624064
https://blog.csdn.net/mu_wind/article/details/102758005