【Spring Data】JPA 审计功能的使用
1. 审计是什么
文字解释:透明地跟踪谁创建或更改了实体以及创建、更改发生的时间。 代码解释:
// 模拟场景:修改文章标题和内容
Article article = new Article();
article.setId(1);
article.setTitle("new title");
article.setContent("new content");
// 手动设置修改日期
article.setModifiedDate(LocalDateTime.now());
// 手动设置修改人员,此处按用户名
article.setModifiedOperator("jack");
ArticleRepository.save(article);启用审计功能后,代码量减少
// 修改文章标题和内容
Article article = new Article();
article.setId(1);
article.setTitle("new title");
article.setContent("new content");
ArticleRepository.save(article);2. 在 JPA 中的使用
2.1 跟踪创建日期和修改日期
此场景用到 3 个注解 创建日期字段添加 @CreatedDate 修改日期字段添加 @LastModifiedDate 类上添加 @EntityListeners
@Entity
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class)
public class Article implements Serializable {
// 无关代码略
@CreatedDate
private LocalDateTime createdDateTime;
@LastModifiedDate
private LocalDateTime updatedDateTime;
}数据类型选用 LocalDateTime,当然 Date、 Instant 等均可 最后在启动类或配置类上添加 @EnableJpaAuditing 注解
2.1.1 @EntityListeners 的说明
注解名已经说明了作用:实体监听。 具体作用:对标有此注解的实体类的 CRUD 操作进行监听(查询操作也是可以审计的)。该注解仅有一个
Class 数组类型的 value 属性,用于指定监听器类,上述代码中使用了 AuditingEntityListener 这个由 JPA
提供的监听器,审计功能实际就是通过该类中的方法奏效的
@PrePersist
public void touchForCreate(Object target) {Assert.notNull(target, "Entity must not be null");
if (this.handler != null) {AuditingHandler object = (AuditingHandler) this.handler.getObject();
if (object != null) {object.markCreated(target);
}
}
}
@PreUpdate
public void touchForUpdate(Object target) {Assert.notNull(target, "Entity must not be null");
if (this.handler != null) {AuditingHandler object = (AuditingHandler) this.handler.getObject();
if (object != null) {object.markModified(target);
}
}
}不难看出,新增操作会触发 touchForCreate 方法,更新操作会触发 touchForUpdate 方法

查看该类结构可以发现,JPA 提供的 AuditingEntityListener 监听器仅监听了 CRUD 中的 C(新增)、U(更新),并未监听 D(删除)
操作,而且代码是固定的,无法整合业务,这就需要定制审计监听器了,方法见后文
2.2 跟踪创建者和修改者
同上,创建者字段添加 @CreatedBy 注解,修改者字段添加 @LastModifiedBy 字段 数据类型均选用 String,表示被跟踪者的用户名。也可以为
Long(保存 ID)、对象
@Entity
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class)
public class Article implements Serializable {
// 无关代码略
@CreatedBy
private String createdOperator;
@LastModifiedBy
private String modifiedOperator;
}在此基础上,审计基础设施需要以某种方式了解当前主体,为此,JPA 提供了一个 SPI 接口: AuditorAware(Servlet 模式,WebFlux 模式则为
ReactiveAuditorAware),以告知基础架构当前与应用程序交互的用户或系统是谁。通用泛型 T 定义了标有 @CreatedBy 或
@LastModifiedBy 的属性必须是什么类型。
2.2.1 写法一(以 Bean 的形式创建)
@EnableJpaAuditing
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class JpaConfig {
@Bean
public AuditorAware<String> auditorProvider() {
// TODO 获取当前主体 do something...
return ()-> Optional.of("username");
}
}泛型 T 必须和标有 @CreatedBy、@LastModifiedBy 属性的类型一致,当然这两个属性的类型也要一致
2.2.2 写法二(实现 AuditorAware 接口)
@Component
public class CustomAuditorAware implements AuditorAware<String> {
@Override
public Optional<String> getCurrentAuditor() {
// TODO 获取当前主体 do something...
return Optional.of("username");
}
}2.2.3 写法三(基于 Spring Security 的实现)
Spring Security 中提供了 SecurityContextHolder.getContext() 方法用于获取当前主体
@Component
public class SpringSecurityAuditorAware implements AuditorAware<User> {
@Override
public Optional<User> getCurrentAuditor() {return Optional.ofNullable(SecurityContextHolder.getContext())
.map(SecurityContext::getAuthentication)
.filter(Authentication::isAuthenticated)
.map(Authentication::getPrincipal)
.map(User.class::cast);
}
}当然,编写上述代码的前提是将 createdOperator、modifiedOperator 属性的类型设为 User。
3. 自定义审计监听器
上文的实体类为 Article ,故监听器命名为 ArticleAuditingListener。编码前还需要了解几个 Hibernate 支持的回调注解
注解描述 @PostLoad 在将实体加载到当前持久性上下文或刷新实体后执行。@PostPersist 在实体管理器持久化操作实际执行或级联后执行。在执行数据库
INSERT 后调用此调用。@PostUpdate 在数据库更新操作之前执行。@PostRemove 在实体管理器删除操作实际执行或级联后执行。此调用与删除操作同步。
以上均为 @Target({ElementType.METHOD}),只能标在方法上 一句话概括:执行时机分别对应实体的 CRUD 操作,@PostXxx 表示后执行,与之对应的
@PreXxx 同理,表格不再列出,需要注意一点,不存在 @PreLoad 注解,因为逻辑上无意义,因此一共有 7 个回调注解
开始编码
@Slf4j
public class AuditEntityAuditingListener {
@PostLoad
private void postLoad(AuditEntity entity) {log.info("查询后做些什么 {}", entity);}
@PrePersist
private void prePersist(AuditEntity entity) {log.info("插入前做些什么 {}", entity);}
@PostPersist
private void postPersist(AuditEntity entity) {log.info("插入后做些什么 {}", entity);}
@PreUpdate
private void preUpdate(AuditEntity entity) {log.info("更新前做些什么 {}", entity);}
@PostUpdate
private void postUpdate(AuditEntity entity) {log.info("更新后做些什么 {}", entity);}
@PreRemove
private void preRemove(AuditEntity entity) {log.info("删除前做些什么 {}", entity);}
@PostRemove
private void postRemove(AuditEntity entity) {log.info("删除后做些什么 {}", entity);}
}之后在 @EntityListeners 中配置
@Entity
@EntityListeners({AuditingEntityListener.class, ArticleAuditingListener.class})
public class Article implements Serializable {
// 无关代码略
@CreatedDate
private LocalDateTime createdDateTime;
@LastModifiedDate
private LocalDateTime updatedDateTime;
}4. AbstractAuditable 抽象类
还有一个方便的基类 AbstractAuditable,您可以扩展它以避免手动实现接口方法的需要。但这样做会增加实体类与 Spring Data
的耦合,这可能是您想要避免的事情。通常,首选基于注释的方式来定义审计元数据,因为它侵入性更小且更灵活。
新建实体类 Customer,继承 AbstractAuditable<U, PK> U 表示创建者和修改者字段的类型,必须为引用类型,因为这两个字段被
@ManyToOne 标记
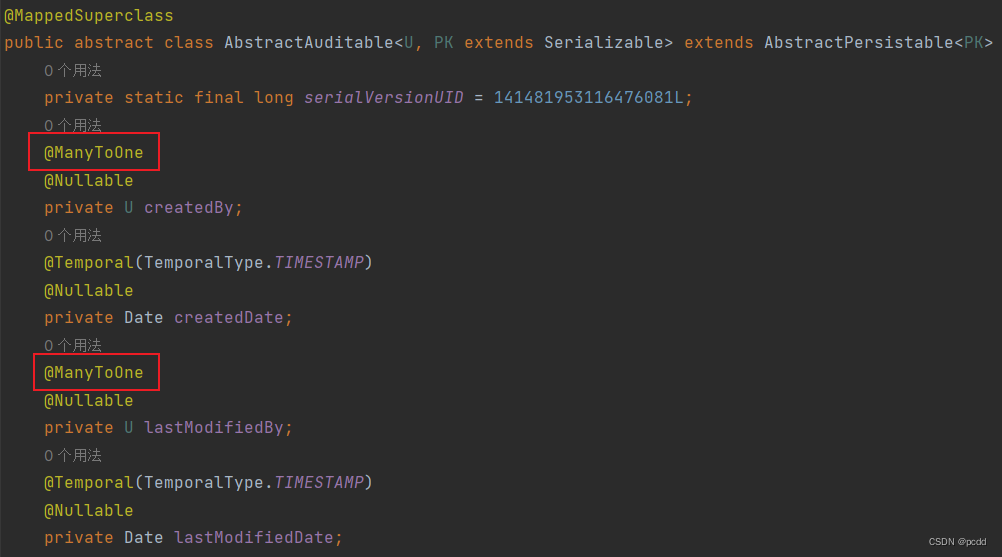
PK 表示主键的类型
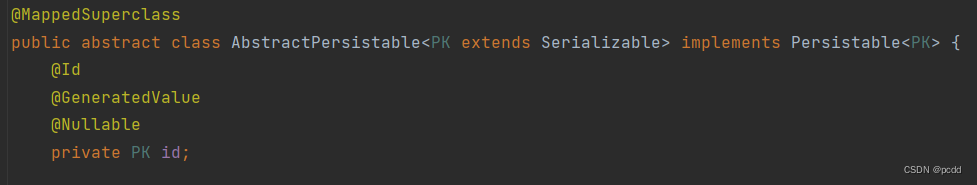
最终结果
@Data
@Entity
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class)
public class Customer extends AbstractAuditable<Customer, Long> {
// 省略了 id、createdBy、createdDate、lastModifiedBy、lastModifiedDate,因为已被继承
private String name;
}由于 U 指定为 Customer,因此 AuditorAware 中的 T 也要指定为 Customer
@EnableJpaAuditing
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class JpaConfig {
@Autowired
CustomerRepository customerRepository;
/* @Bean
public AuditorAware<String> auditorProvider() {return () -> Optional.of("admin");
} */
@Bean
public AuditorAware<Customer> auditorProvider() {
// 这里需要确保 id=1 的记录在程序运行前就已在 customer 表中
return ()-> customerRepository.findById(1L);
}
}之前定义的 Bean 需要被替换,只能保留一个,上文的 Article 实体类的 2 个字段也要做兼容处理,类型修改为 Customer ,这也说明 JPA
项目的审计字段类型要保持类型统一
观察 JPA 生成的 Customer 表结构,发现 createdBy、lastModifiedBy 字段被设为外键了,实际存储的是 customer 的 ID
create table customer (
id bigint not null primary key,
created_date datetime(6) null,
last_modified_date datetime(6) null,
name varchar(255) null,
created_by_id bigint null,
last_modified_by_id bigint null,
constraint FK1m3j3p1e2rd5ppt4wpwqjv5rh
foreign key (last_modified_by_id) references customer (id),
constraint FKitafsntr2a6dfn48t56h73puw
foreign key (created_by_id) references customer (id)
);最后使用 CustomerRepository 进行 CRUD 操作,观察审计效果
通过上面的说明,总结 AbstractAuditable<U, PK> 的优缺点
优点:节省代码,让项目中的所有实体类均继承该类(类似
BaseEntity),可以省去定义 5 个字段:id、createdBy、createdDate、lastModifiedBy、lastModifiedDate 缺点:
实体类与 Spring Data 耦合
无法指定 id 类型,id 只能为自增,而且是 GenerationType.AUTO 并非 GenerationType.IDENTITY,也就是说每多一个 xx 实体类还需要额外一个
xx_seq 表来维护主键的自增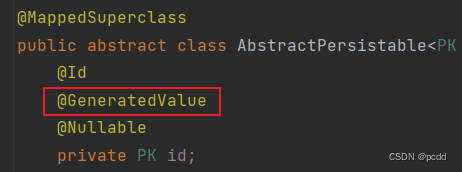
不够灵活,审计字段的名称无法修改、createdDate、lastModifiedDate 的类型只能为 Date